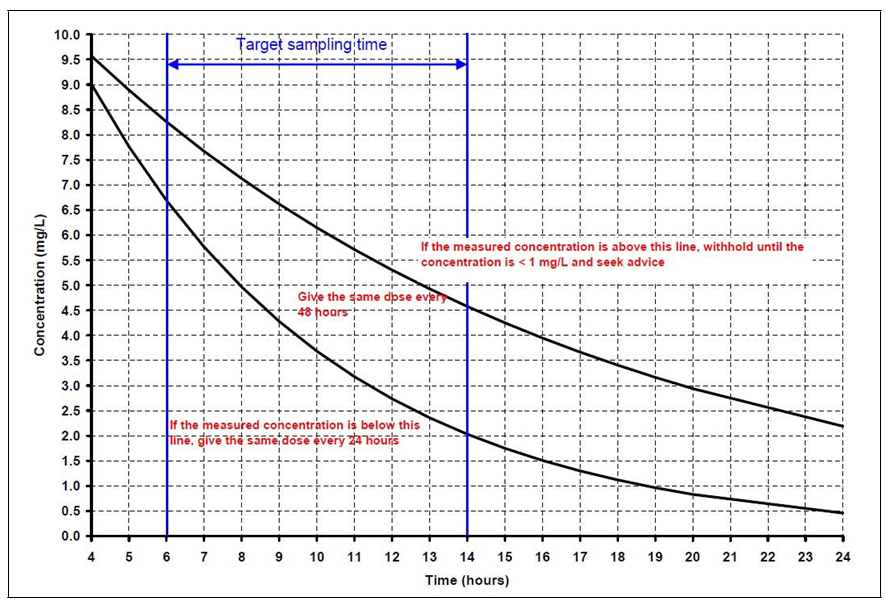
Nephrotoxicity:
- Dose-dependent: further rise in creatinine/oliguria will lead to gentamicin accumulation
- Ensure good hydration, avoid co-prescription nephrotoxic medication (eg. furosemide)
Ototoxicity
- Dose-independent; related to drug accumulation in the inner ear
- Associated with prolonged use (usually >10 days but may be >72 hours).
- Symptoms: new tinnitus, dizziness, poor balance, hearing loss or oscillating vision.
If ototoxicity/vestibulotoxicity is suspected, discontinue aminoglycoside therapy, refer to ENT for assessment and call microbiology to discuss alternative antimicrobials.
If therapy continues for >7days, obtain baseline audiometry then repeat monthly.