Key principles
- Primary goal is rapid definitive haemorrhage management.
- Excessive blood pressure causes bleeding:
- Target MAP 50–60.
- Consider MAP 60–70 in elderly or isolated head injury.
- Use volume to maintain blood pressure.
- Correct coagulopathy early.
- DO NOT GIVE CRYSTALLOID PRIOR TO DEFENITIVE HAEMORRHAGE CONTROL.
- DO NOT GIVE VASOPRESSORS PRIOR TO DEFINITIVE HAEMORRHAGE CONTROL.
- Manage hyperkalaemia and hypocalcaemia.
- Maintain normothermia.
- Minimise patient movement to prevent clot disruption.
- Communicate physiology regularly with surgeons and team.
Equipment
- Airway Trolley.
- Rapid Infuser:
- May require a dedicated practitioner.
- Cell salvage.
- Large volume central and peripheral access.
- Underbody warmer.
- Warm theatre (ambient temperature 25 degrees celsius).
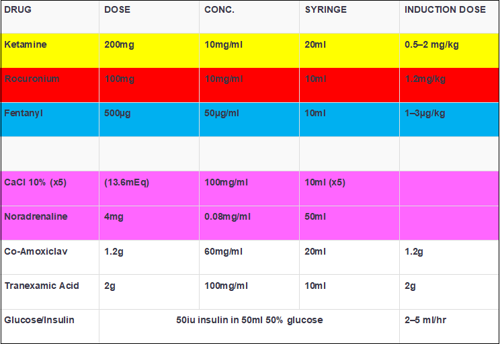
Drugs to draw up
Monitoring
- Standard AAGBI monitoring.
- Invasive blood pressure monitoring only if it does not delay time to haemorrhage control.
Blood Management
- Declare code red/major haemorrhage as per hospital protocol.
- Ensure blood is available and checked prior to induction.
Induction and maintenance of anesthesia
- Pre-oxygenate:
- Consider OPA + 2 x NPA to optimise.
- Manual in-line cervical spine.
- Consider reverse Trendelenburg position.
- Anticipate hypotension on induction:
- Ensure rapid infuser connected, functional and loaded with blood and products.
- Reduce drug doses and volatile concentration:
- (aim 0.3–0.5 MAC until haemodynamically adequate).
- Antibiotics
- Aim to deliver 300–500µgfentanyl slowly over first half an hour.
Blood pressure and coagulopathy management
Blood pressure
- Cycle BP at one minute intervals.
- Target: MAP 50–60 mmHg (60–70 in elderly/isolated head injury).
- Use volume and calcium chloride (centrally) to maintain MAP.
Coagulation
- Target an empiric red blood cell:plasma:platelet ratio of 1:1:1.
- Tranexamic acid 1g (may have been given by pre-hospital team).
Maintain ionised calcium > 1.0mmol/l.
Post definitive Haemhorrage control
- Aim to restore normal physiology.
- Use base deficit and lactate to guide volume resuscitation.
- ROTEM may be used to deliver targeted coagulopathy management.
- Consider noradrenaline, if required, only once circulating volume is restored and definitive haemorrhage control achieved.




