Concentrations are meaningless unless the dose and sample time are recorded accurately
If creatinine clearance is 21mL/min or greater
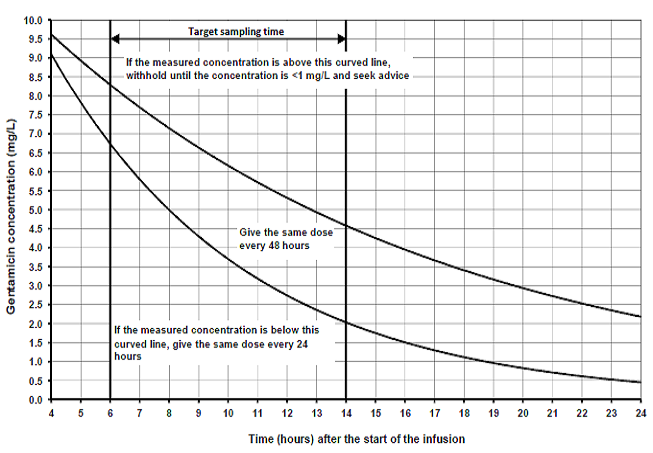
- Take a blood sample 6 to 14 hours after the start of the first gentamicin infusion.
- Record the exact time of all gentamicin samples on the gentamicin prescribing chart AND on the sample request form.
- Record the serum concentration on the gentamicin prescribing chart.
- Plot the concentration measurement on the graph and reassess the dose/dosing interval as indicated.
- This will indicate one of 3 options:
- continue the present dosage regimen
- adjust the dosage interval
- withhold and resample after 24 hours
If creatinine clearance is less than 21mL/min
- Take a blood sample 24 hours after the start of the first gentamicin infusion.
- Record the exact time of all gentamicin samples using the gentamicin prescribing chart AND on the sample request form.
- If therapy is to continue, take additional blood samples at least every 24 hours and give a further dose once the measured concentration is below 1mg/L.
General points
- Document the action taken in the medical notes and on the gentamicin prescribing chart.
- Undertake pre-prescribing checks to assess the risk of renal toxicity and ototoxicity.
- Prescribe the next dose as appropriate.
- Seek advice from pharmacy or microbiology if you are unsure how to interpret the result or if the concentrations are very low. Doses up to 600mg may be required for some patients.
- If a blood sample is not taken, is lost or is taken at wrong time and if there is any concern about the patient’s renal function, take a sample 20 to 24 hours after the start of the gentamicin infusion and wait for the result before giving the next dose. Otherwise, take a blood sample after the next dose.
If the measured concentration is unexpectedly HIGH or LOW, consider the following:
- Were dose and sample times recorded accurately?
- Was the correct dose administered?
- Was the sample taken from the line used to administer the drug?
- Was the sample taken during drug administration?
- Has renal function declined or improved?
- Does the patient have oedema or ascites?
If in doubt, take another sample before re-prescribing and/or contact pharmacy for advice


